
Sample and Production Merchandising.
Sample and production merchandising is a part of product merchandising. The buyer mainly requires making and approving samples for their approval. Sample and Production Merchandisers makes the design, color, size, etc. right to ensure the buyer’s satisfaction and finalizes the order. After receiving an order, we ensure the supply of raw materials, schedule production, and carry out quality assurance for effective management of the production process. Sample and Production Merchandisers monitor every step of production and after completing the production within the stipulated time the product reaches the customer on time. Efficient management of sample and production merchandisers is key to a successful business.
Responsibilities of the sample & Production Merchandiser.
Act as a bridge between the sourcing merchant, Local buying office & technical team, and production team.
- Ensure fabric, trims, and accessories are storge on time.
- Coordinate sample development, including proto samples, fit samples, size sets, and pre-production (PP) samples.
- Keep the sourcing merchant updated on the status of sample development.
- Ensure samples meet the buyer’s specifications and quality standards.
- Coordinate the bulk production from order placement to shipment.
- Ensure that production meets the agreed-upon timelines, quality, and budget.
- Address any issues in production to prevent delays.
- Facilitate communication between various teams, such as pattern, cutting, washing, and production.
Work process for sample and production merchandiser.
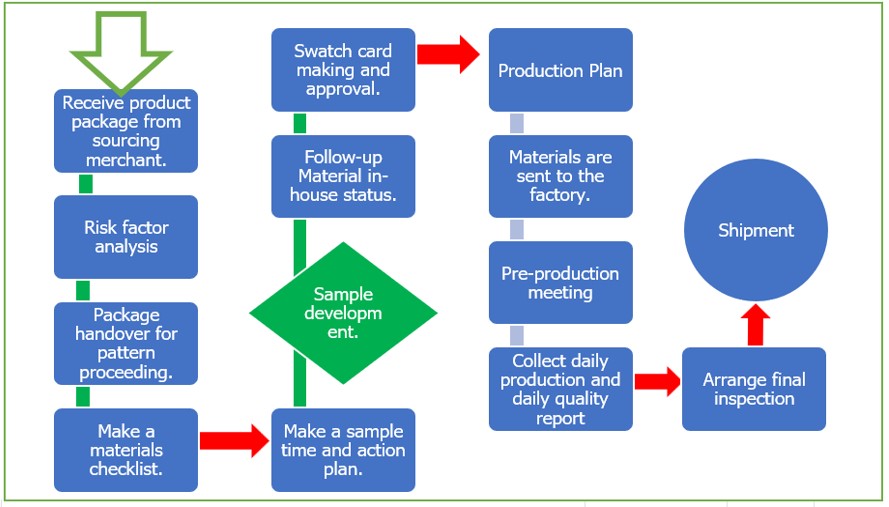
Sample development & Coordination:
Overview:
- Concept of sampling.
- Definition of sampling.
- Purpose of sampling.
- Importance of sampling.
- Why Multiple samples are necessary.
Concept of Sample
- Samples have to decide the ability of an exporter.
- Samples consist of fashion design & fittings of any item.
- Sample helps in optimizing the process parameter for mass production and also can aid in eliminating bottlenecks in bulk production.
- Samples understanding and fulfilling customer needs.
- Samples confirming measurements and fabric requirements.
- Samples fulfillment of fabric consumption & determining the cost of garments.
- Integrating the overall performance of an apparel export order.
Definition of sampling.
Sampling is an important process in the readymade garment industry. A prototype sample has to allow designers, buyers, and manufacturers to review and approve the design, fit, fabric, trim, and overall quality of the garment. The sampling stage includes proto samples, fit samples, size sets, and pre-production samples, ensuring that the final product meets the buyer’s expectations.
- Purpose of sampling.
Sampling is an important process in the ready-made garments industry to ensure that the final product meets the customer’s expectations in design, fit, fabric, and quality before mass production.
- Key purposes include:
- Design Validation.
- Fit and Sizing.
- Material and Quality Check.
- Production Feasibility.
Importance of sampling.
Sampling plays a crucial role in the readymade garments industry for several important reasons:
- Quality Assurance.
- Fit and sizing accuracy.
- Cost and Time Efficiency.
- Buyer Approval:
- Production Feasibility:
Thus, sampling is essential for delivering high-quality garments efficiently and in alignment with buyer expectations.
Why Multiple samples are necessary.
In the readymade garments industry, multiple samples are required to ensure the final product meets design, quality, and production requirements before bulk manufacturing. Each sample serves a specific purpose, such as assessing the prototype, testing the fit, comfort, and measurements, producing a size set, and confirming the pre-production (PP) sample. These stages allow for necessary adjustments, reducing risks of errors, defects, or dissatisfaction during large-scale production and ensuring a smooth and efficient manufacturing process.
Sample procedure timeline.
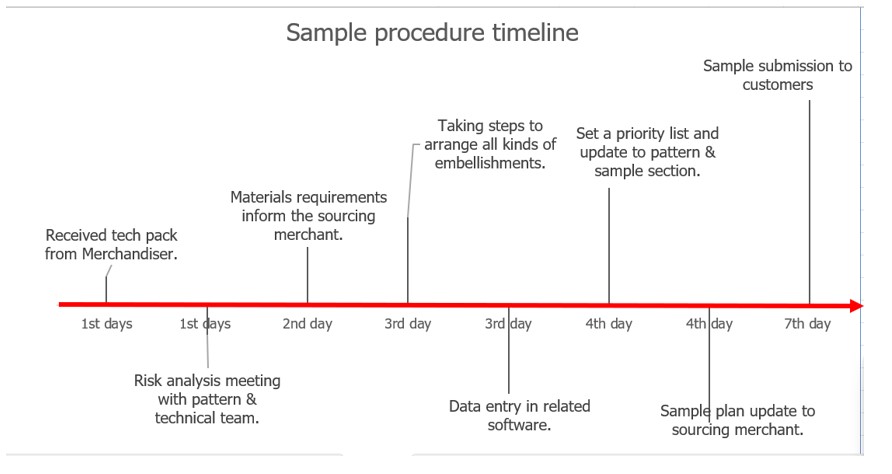
Procedure for Sample Preparation.
Overview:
- What are the things to observe in making the 1st sample?
- Type of Samples.
- Samples type-wise submission deadline..
What are the things to observe in making the 1st sample?
- BOM sheet and original sample if available.
- Pattern making as per measurement.
- Check the pattern is right between the construction sheet & the original sample.
- Inform to pattern section fabric shrinkage, and twisting before starting the pattern.
- Make a T & A sample submission deadline.
- Update all risk analysis factors to sourcing merchant and other logistics sections.
- Arrange fabric and materials.
- Requisition or log In for sample sewing.
- Confirm that both the sample quality and fittings satisfy the requirements of the customer.
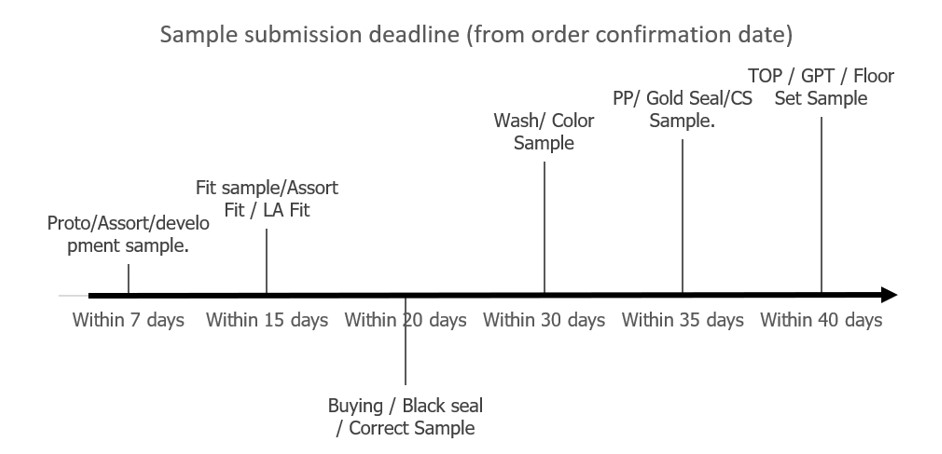
Type of sample.
- Proto/Assort/development sample.
- Fit sample/Assort Fit / LA Fit
- Buying / Black seal / Correct Sample
- Wash/ Color Sample
- PP/ Gold Seal/CS Sample.
- TOP / GPT / Floor Set Sample
Sample submission deadline (from order confirmation date)
Production Planning and Order Management.
Overview:
- Importance of sample and production merchandiser.
- Working Procedure Timeline as a Sample and Production Merchandiser.
- Skills required for a sample & production merchandiser
- Follow-up activities of bulk production.
- Washing follow-up.
- Quality Control:
In the ready-made garments industry, a production merchandiser plays an important role in ensuring that products are manufactured and delivered according to client requirements, timelines, and cost-effectiveness. A designated time limit must be set to facilitate the thorough and proper execution of these activities.
- What is the duration required for obtaining fit sample approval?
- What is the timeframe for the approval of WASH and similar samples?
- What is the estimated time for the approval of the PP sample?
- Expected timeline for raw materials in-house?
- What is the expected duration of the production plan?
- Expected timeline for the PP meeting for bulk production?
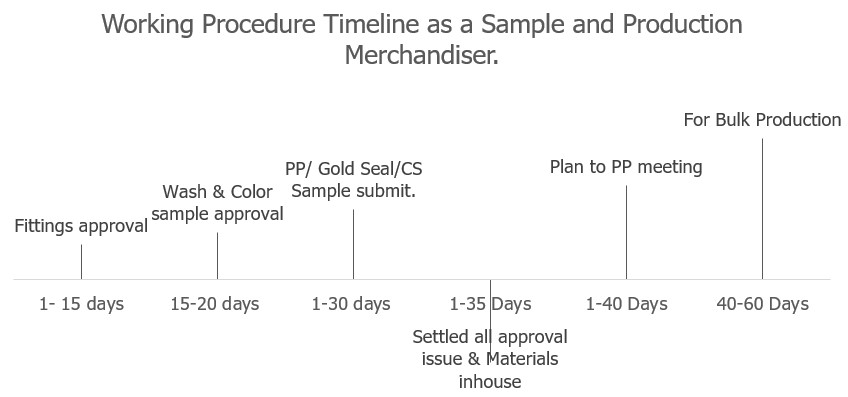
Working Procedure Timeline as a Sample and Production Merchandiser.
Skills required for a sample & production merchandiser.
- Strong communication and negotiation skills.
- Knowledge of fabric, trim, and garment manufacturing processes.
- Expertise in time management, costing, and budgeting.
- Quality control and problem-solving ability.
- Proficiency in software used to track production and orders (Oracle systems).
- This process ensures a streamlined production workflow and helps deliver high-quality garments while meeting client expectations.
Sourcing and Procurement.
- Material Sourcing: For accurate material sourcing, sample and production merchandisers will give accurate consumption of fabrics, trims, and other raw materials as soon as the first sample is produced. It must also ensure that the materials meet the specifications (quality, color, etc.) required for the order.
Production planning.
- Production merchandisers prepare a production plan that includes timelines, capacity bookings with factories, and a detailed schedule for each stage of manufacturing. It ensures timely delivery.
Order Execution and Monitoring.
Production coordination: The merchandiser coordinates with the factories, providing them with technical packs (tech-packs), materials, and instructions for production.
Washing follow-up: Washing follow-up is a critical part of the production process for garments, as merchandisers need to understand washing requirements as well as the following skills required:
- Technical Knowledge: Understanding different washing processes and their effects on fabrics is essential. The merchandiser must be able to communicate effectively with the washing team and troubleshoot problems.
- Problem Solving: The ability to quickly identify and resolve issues during washing is crucial to avoid delays and maintain quality.
Wash follow up:
- The merchandiser gathers detailed information about the type of washing (e.g., stone wash, enzyme wash, acid wash, bleach, etc.) and provides it to the washing department.
- Wash Samples and Approval: The merchandiser works with the washing team to create wash samples, which are then sent to the client for approval. Any revisions in the wash process are communicated back to the team.
- Coordination with the washing unit.
- Planning the Washing Schedule: The merchandiser coordinates with both the production and washing units to ensure the washed garments are completed on time, without causing delays in the overall production schedule.
Final Inspection:
Merchandisers will know the exact time of completion and final inspection of goods from the factory and ensure final inspection accordingly for timely shipment.
- Arrange a final inspection of finished garments before packaging.
- Ensure packaging materials meet buyer’s specifications (eg, barcode, poly bag, carton).
- Ensure shipping arrangements including logistics to meet delivery timelines.
Conclusion.
The ready-made garments industry relies heavily on sample and production merchandising activities to ensure product quality, timely delivery, and client satisfaction. Merchandisers coordinate with buyers, designers, suppliers, and manufacturers, manage material sourcing, production planning, quality control, and communication, oversee washing, finishing, and packaging, and maintain consistency to streamline operations and meet aesthetic and functional requirements.
Author: Abdul Aziz
Head of Sample & Innovation
Standard Group (MH)
