
Production Planning and Control.
Production planning and control are techniques for planning a chain operation. They determine what, how much, and when to produce based on market demand and production capacity. On the other hand, production control focuses on monitoring and managing the actual production process to conform to the production plan.
We know that production is a transformational process. So, planning and control involves managing and allocating raw materials, human resources, work centers, machinery, and production processes. The more impurity-free and even distribution this process ensures, the more productivity increases. Production must be planned and controlled by ensuring optimum utilization of resources such as workforce, machinery, materials, money, and time. Production planning and control is an indispensable method in the garment industry. An efficient infrastructure is established for production planning and control.
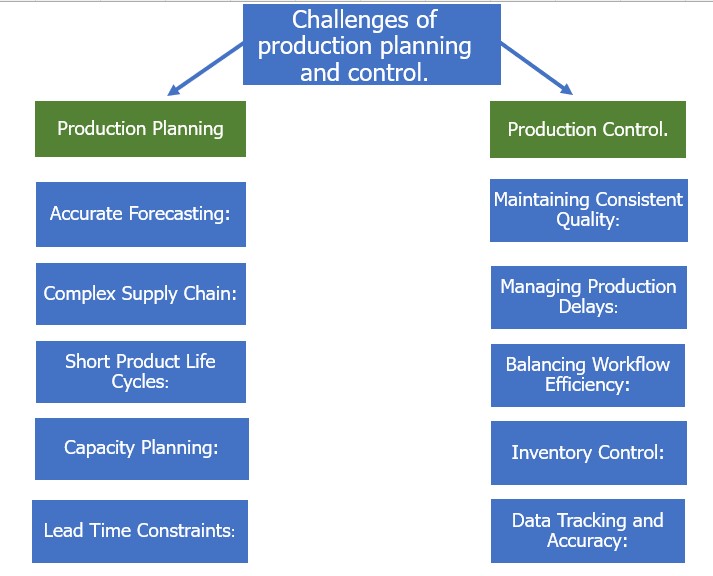
SOP for production planning and control?
Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) are crucial for production planning and control in the apparel industry for several reasons. Production is a transformational process, so it is essential to plan and control it. The allocation method of raw materials, human resources, work centers, and machinery should be planned appropriately. To meet the customer’s needs within a short lead time. This SOP applies to the planning and control process involved in garment production. which covers all stages from order receipt to final product shipment. A structured method for every job where there is no slight deviation in fabric cutting, stitching, or finishing. Production planning and control improve efficiency, maintain quality, reduce costs, and ensure safety and compliance in the apparel industry. With SOPs, it is easier to maintain the accuracy and coordination required to run a successful garment manufacturing operation.
Workflow chart for production planning and control.
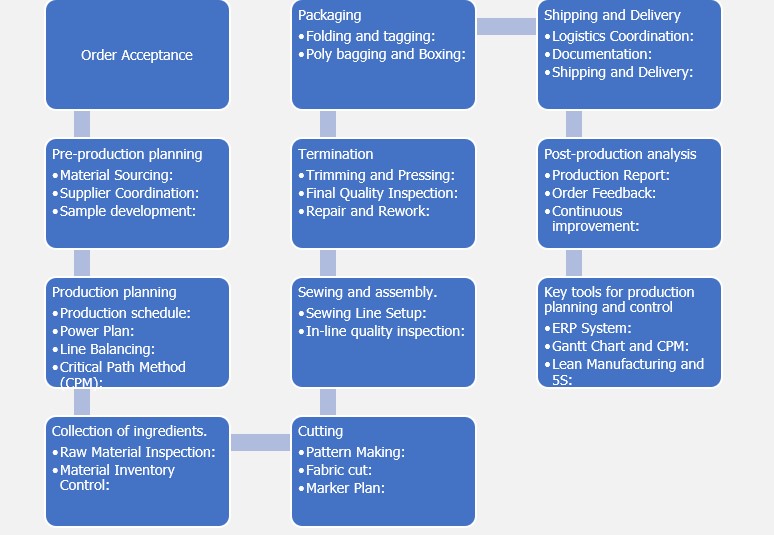
The efficient organizational structure of production planning and control.
A strong organizational structure helps determine the right SOPs, ensuring clear responsibilities, streamlined communication, and quick decision-making.
Clarify Roles and Responsibilities: Define who is responsible for what, which reduces confusion and overlap of duties
Efficient communication: Makes proper coordination between various departments, such as procurement, production, quality, and shipping.
Resource Optimization: Helps allocate resources such as workforce, machinery, and materials based on production needs and priorities.
Quick Decision Making: Ensures quick resolution of any production bottlenecks, delays, or inefficiencies.
Accountability: Clear hierarchy and defined roles ensure accountability at every stage of the production planning process. After confirming these things, the organizational structure has to be created.
Organ chart for production planning and control management.
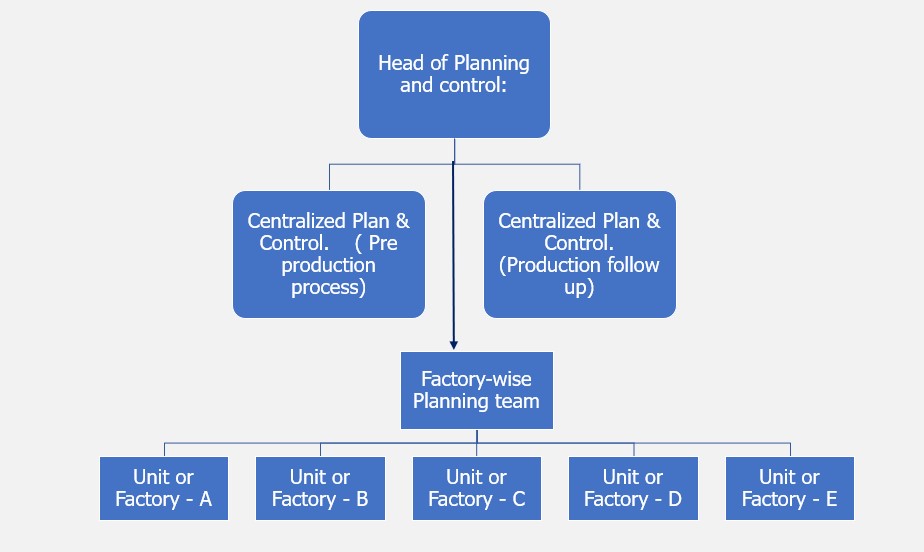
Key Responsibilities of the Head of Planning:
The Production Planning and Control Head is an important position that ensures an efficient production process, timely product delivery, and optimum resource utilization.
Strategic Planning: Production schedules and strategies must be consistent with order deadlines, factory capacity, and customer requirements in strategic planning.
Orders should be allocated based on workforce, machine availability, and factory capacity by reviewing existing orders.
Ensure that factory capacity is not exceeded and production volume is planned for each line, booking orders accordingly.
We need to ascertain the feasibility of orders based on current capacity and resource availability.
Monitor lead times for fabric, trim, and accessories to align with
Create a critical path for orders to identify key production milestones. Monitor the critical path to ensure timely execution at each stage (e.g., sample approval, fabric distribution, cutting, sewing, and finishing).
Key Responsibilities of the Centralized Planners ( Pre-production):
Production Planning and Scheduling.
Resource Allocation and Optimization:
Monitoring and controlling production processes.
On-Time Delivery Rate:
Production Efficiency:
Factory Utilization:
Defect Rate:
WIP Levels:
Resource Utilization:
Key Responsibilities of the Factory-wise Planning Team:
Factory Production Scheduling:
Line Planning:
Order Allocation:
Capacity Assessment:
Resource Allocation:
WIP Tracking:
WIP Control:
Daily Production Tracking:
Efficiency Monitoring:
Order Progress Monitoring:
Quality Control Integration:
Defect Management:
Cross-Department Communication:
Material Availability Monitoring:
Material Usage Efficiency:
Inventory Control:
Problem-Solving:
Bottleneck Identification and Management:
Head of Production Planning and Control (PPC).
Monitor lead times for fabric, trim, and accessories to align with
Create a critical path for orders to identify key production milestones. Monitor the critical path to ensure timely execution at each stage (e.g., sample approval, fabric distribution, cutting, sewing, and finishing).
Central Planner (Pre-Production):
The centralized Planner (Pre-Production) will initially assess the status of product sample approval planned by the Chief Planner and arrange for goods input after confirming the overall status of raw materials to facilitate input planning.
We will observe whether the Fit/PP samples are approved, or if the line will be interrupted for their approval.
Whether there are any complications regarding the approval of fabric or other raw materials or whether there will be any problems with bulk production.
Coordinate with the procurement team to order raw materials promptly.
Ensure the fabric, trim, and accessories are in-house based on the Bill of Materials (BOM).
Monitor and plan lead times for fabric, trim, and accessories to align with the production schedule:
Track inventory of raw materials and maintain accurate records of fabric and trims issued to the production floor.
Avoid stockouts by ensuring the timely availability of materials required for production.
Plan the production volume for each line and ensure that the factory does not overbook its capacity.
Central Planner (Post-Production):
The centralized planner (Post-production) will primarily oversee the production of products the chief planner plans.
Is there productivity according to SMV? Will the style input meet the buyer’s deadline?Make sure productivity is not disrupted for any reason and that the swing is completed within the specified budget.
Assess factory capacity by reviewing available workforce, machine availability, and existing orders.
Plan the production volume for each line and ensure that the factory does not overbook its capacity.
Create a Master Production Schedule (MPS) outlining each order’s start and finish dates.
The factory planning team and I ensure daily production output is met to achieve planned targets.
Track real-time production progress using visual boards or production software.
Maintain WIP records to track garments at each production stage (e.g., cutting, sewing, and finishing).
Ensure smooth movement of semi-finished products between different stages without delay.
Implement a FIFO (First In, First Out) system to maintain production flow.
What is the style changeover time & reason?
The time it takes between the last output of the current line style and the first output of the new line style is called Style Changeover Time. Style changeover is a regular thing in the apparel industry. Due to the competitive market, short lead time, and small qty.
Reason for style change over time?
Most are due to inadequacies in the supply chain or for sample approval. Suppose you plan a style input on the 5th of March & and also prepare accordingly. The raw material not arriving or the PP sample requiring approval will cause a longer time for the style changeover.
Does style changeover time affect production planning & control?
Style changeover time has a devastating effect on the swing line.
Delayed output will cost more time and cause the target to fail.
Less productivity and target failure result from delayed output.
The workforce will be idle for a long time. As a result, the line’s loss time will increase, and the average performance will worsen. On the other hand, small and urgent orders will face shipment failure.
The sewing line will not be able to meet its fixed costs, and the company will suffer financially.
How does control ”style change over time”? by production plan & control.
We should design the production plan to not only plan orders but also control it.
Make sure all raw materials are in-house and necessary samples are approved before starting the new production style.
We have completed all tests of the raw materials.
An appropriate and adequate workforce and machines have been prepared and installed according to the process layout of the line.
If a new style is complex or completely new, then its SOP should be fixed in advance.
All necessary patterns should be prepared.
Back-to-back line Layout to be done. That is, as soon as any one input process in the line is completed, the new order should be started without waiting for the completion of all the processes of the previous order.
Supply chains must be maintained for fabric, thread, zipper, button, lace, label, drawstring, tape, etc..
Conclusion,
The first task of production planning and control is demand forecasting. Production planning and control are important functions for any manufacturing organization. Production planning primarily determines what, how much, and when to produce based on market demand, company resources, and production capacity. An effective production planning and control system is crucial to maintaining operational efficiency, on-time delivery, and product quality in the garment industry. It helps optimize resource allocation, manage inventory levels, streamline workflows, reduce delays, and lower production costs. By monitoring every stage of the manufacturing process, from raw material collection to finished product, production control ensures that deadlines are met while maintaining consistency in quality.
Abdul Aziz
Head of Sample & Innovation (Standard Group-MH)
Content Writer
