
Quality assurance and control: learn in detail.
Many people think that quality assurance and control are the same thing. But although the two words are the same, the definitions are completely different. Assurance is a proactive approach and control is an inspection approach. We consider both as essential processes in the industry, which are crucial in delivering garments that meet customer expectations and regulatory standards. Although people often use both terms interchangeably, they mean distinct approaches with unique objectives and methods. In this article, we will know what is quality assurance. And what is quality control? Now come to the detailed discussion.
Quality Assurance and Initiative Steps learn in detail?
We achieve quality assurance (QA) by ensuring that the desired quality of service or product is reached.
The company can implement certain QA steps in marketing its products or services to achieve customer satisfaction. The steps are as follows-
Planning: Initially, the company should formulate a realistic plan.
Testing: The company should test the quality of the product or service.
Monitoring: Through the steps of QA, the company ensures that it has achieved its specific goals and objectives by successfully implementing quality standards.
Implementation: Need to make a high-performing team to successfully implement the quality standards.”
Quality Control and initiative steps learn in detail?
The text is as follows: “Quality control involves a set of activities that ensure the production of a product or service according to its standards.
To implement a quality control process, one must first fix a standard against which the product’s quality can be judged or measured. Preparing an action plan for activities to produce the product according to the selected standard is necessary. The plans for quality control include:
Checking the raw materials of the product and observing the various stages of the production process
Identifying and solving problems
Gathering information and making decisions
Creating a Quality Control Checklist
Determining raw material demand
Determining to package.
Checking the product quality
Categorizing errors, if any
Coordinating between importers, suppliers, and QC staff”
Elements of Quality Assurance:
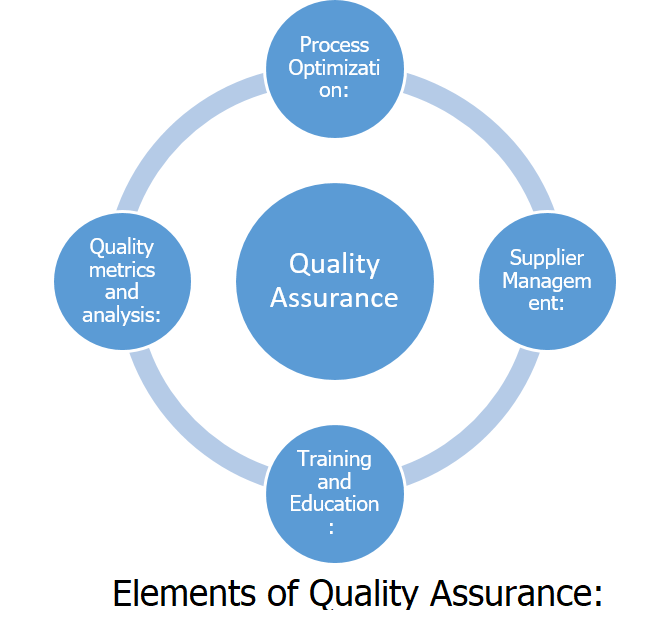
Quality assurance means a proactive approach, which emphasizes prevention rather than problem detection—attempting to eliminate defects by early warning of problems that may occur throughout the garment production process.
Process Optimization: Optimizing processes that lead to manufacturing processes, improved equipment calibration procedures, and best practices for reducing quality risks.
Supplier Management: QA sets internal activities to encompass the entire supply chain.
Training and Education: QA initiatives train on quality standards, procedures, and problem-solving techniques.
Quality metrics and analysis: QA monitors key performance indicators (KPIs) and evaluates process efficiency and product quality.
Bridging the Gap: Integrating QC and QA
Although QC and QA represent distinct approaches to quality management, they are inherently interconnected and complementary.
Elements of Quality Control:
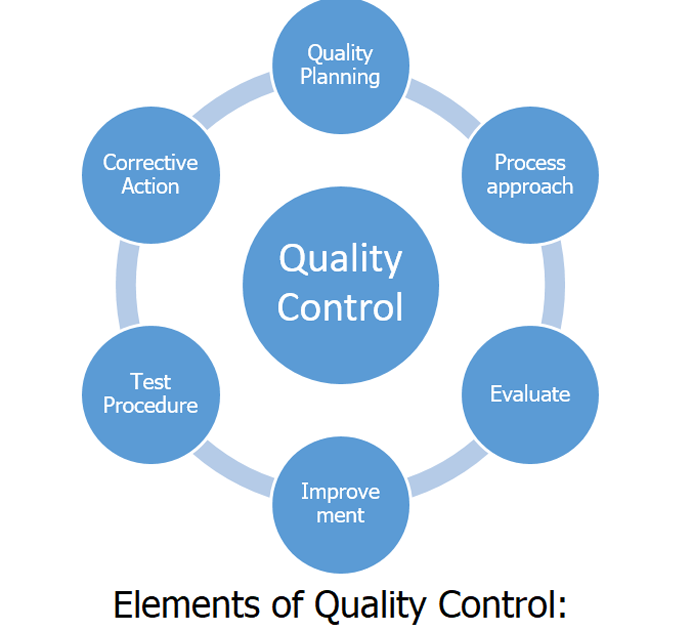
Quality of Product: Quality of Product means appearance, fabric, design, measurement, stitching, cleanliness, presentation, safety, price, and easy availability. QC personnel perform a visual inspection to control the quality of finished garments—checks and control garment defects such as stitching irregularities, fabric defects and color discrepancies with and size discrepancies.
Quality of Process: Quality of Process includes the elements – Man (Man), Machine (Machine), Materials (Materials), and Method (Method). The following methods are used to control the quality of manufactured garments.
Quality Planning
Process approach
Evaluate
Improvement
Test Procedure
Corrective Action
After identifying defects, QC personnel initiate corrective action, which may involve repairing, reworking, or disposing of nonconforming garments. Feedback from QC activities helps identify root causes and implement preventive measures to reduce recurrence.
Quality assurance work procedure learn in detail:
We already know that quality assurance is a method of preventing product defects and, in other words, delivering the product or service to the customer without any problem. According to ISO 9000, it is a part of quality management that ensures that quality requirements are met during the production of products or services.
Proactive process: What kind of problems can occur during product production? Through which the defects of the manufactured products are identified and corrected.
Implementation: Establishing the necessary tools to implement quality standards and monitoring accordingly.
Customer Feedback: Customer feedback is critical in quality assurance. Through this, the company will learn its product or service’s good and bad aspects. It will then take appropriate remedial action to maintain the acceptable quality of the product or service. Customer feedback can be obtained through regular surveys.
Measuring results: Measuring the results of quality assurance of products and services and taking the necessary next steps.
Quality control work procedure learned in detail:
Design, style, color, suitability of material, and fitness of the product for the market to maintain the following points are to be observed.
Documentation Check procedure:
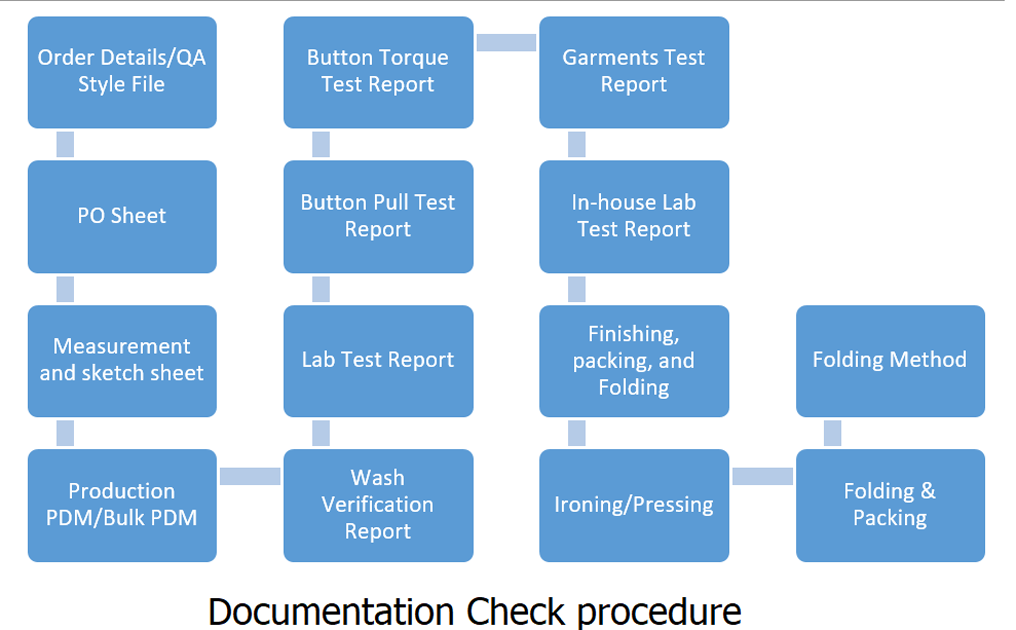
Quality control is done according to the documents sent by the customer. That is why you must first ensure that all types of documents are received and understood. which requires
Order Details and QA File
PO Sheet, Measurement and sketch sheet
Production and Bulk PDM
Wash Verification Report
Lab Test Report
Button Pull and torque Test Report
Garments Test Report
In-house Lab Test Report
Finishing, packing, and Folding
Ironing or Pressing
Folding and Packing
Folding Method
Visual outlook check procedure:
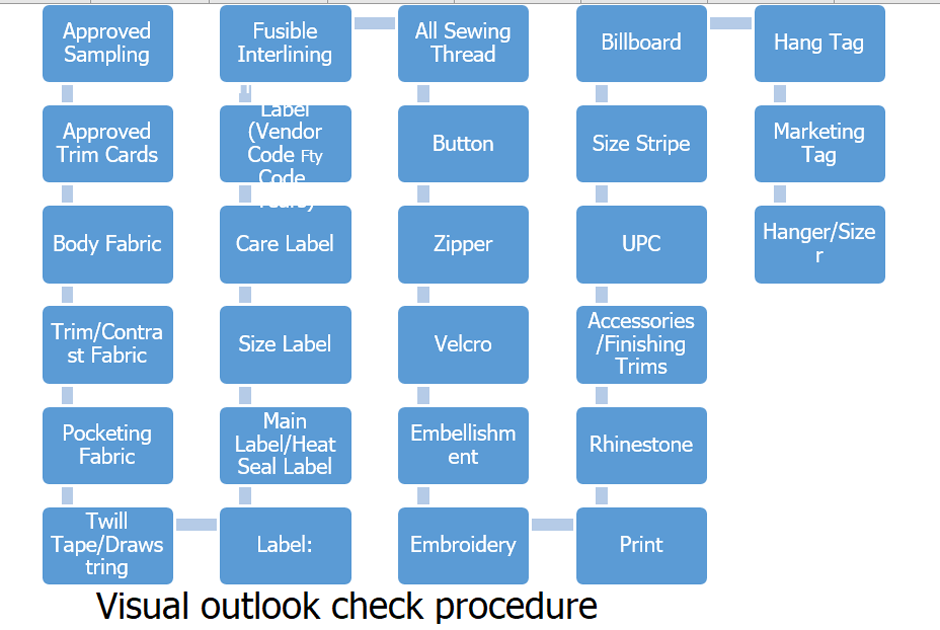
Ensure that the design, raw material, and other accessory embellishments are correct as per the samples sent by the customer.
Approved Sampling and Trim Cards
Body Fabric and Trim orContrast Fabric
Pocketing Fabric
Twill Tape/Drawstring
Label:
Main Label and Heat Seal Label
Size Label and care Label
Tracibilities Label (Vendor Code Fty Code, Years)
Fusible Interlining
All Sewing Thread
Button , Zipper and Velcro
Embellishment or Embroidery. Print and Rhinestone
Accessories and Finishing Trims
UPC
Size Stripe, Billboard. Hang Tag and Marketing Tag
Hanger and Sizer
In-process (Sewing) check procedure:
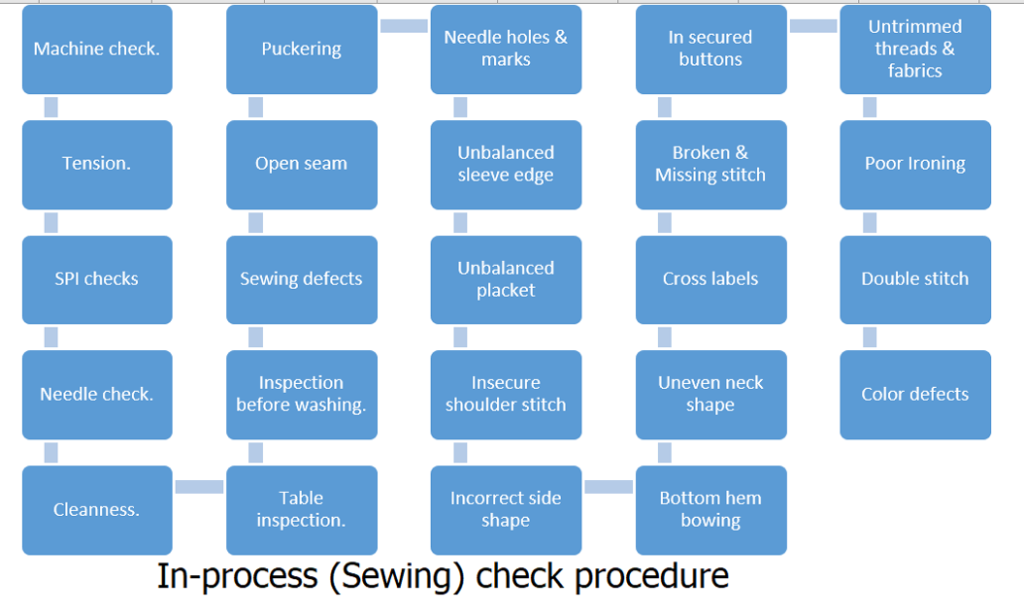
During the swing, ‘In-process quality control’ is conducted by the line QCs through a seven-piece inspection system. For critical operations, 100% of process inspections are performed. The following parameters are also verified in the sewing process.
Machine check.
Needle and Tension check
SPI checks
Cleanness.
Table inspection.
Inspection before washing.
The main focus at the time of process inspection at below points
Sewing defects or Open seam
Puckering, Needle holes and marks
Unbalanced sleeve edge and Unbalanced placket
Insecure shoulder stitch and Uneven neck shape
Incorrect side shape
Bottom hem bowing
Cross labels
Broken & Missing stitch
In secured buttons
Untrimmed threads & fabrics
Poor Ironing
Double stitch
Color defects
Color & Fittings check as approved sample procedure
Garment, wrong color combinations, and mismatching dyes.
Sizing defects and wrong gradation of sizes,
Differences in the measurement of various parts of a garment, like sleeves of XL size for the body of L size garment, can deteriorate the garments beyond repair.
Artistry at stitching quality:
Ensure the sewing stitich is meeting the customers requirement.
Seam check for jump stitch
Check correct thread, size and color are used for stitching.
Per safety norms, all trims and accessories (like drawstrings and beads) are attached to the garment.
Conclusion:
Bangladesh’s ready-made garments are trendy in the global market but the quality system is not satisfactory due to insufficient experience. But lately, many educated unemployed people without a textile background are becoming self-reliant by training in quality control. Quality is an essential component of management systems, each serving distinct yet interrelated purposes within the production landscape. While QC focuses on post-production inspections and defect remediation, QA adopts a proactive stance, emphasizing process optimization, supplier collaboration, and continuous improvement. By harmonizing these approaches and embracing a holistic quality management philosophy, garment manufacturers can elevate product quality, enhance customer satisfaction, and sustain long-term competitiveness in the dynamic global market.
Author
Abdul Aziz
Head of Innovation
Standard Group-
